Sustainable Farming in Indian Agriculture
Introduction :
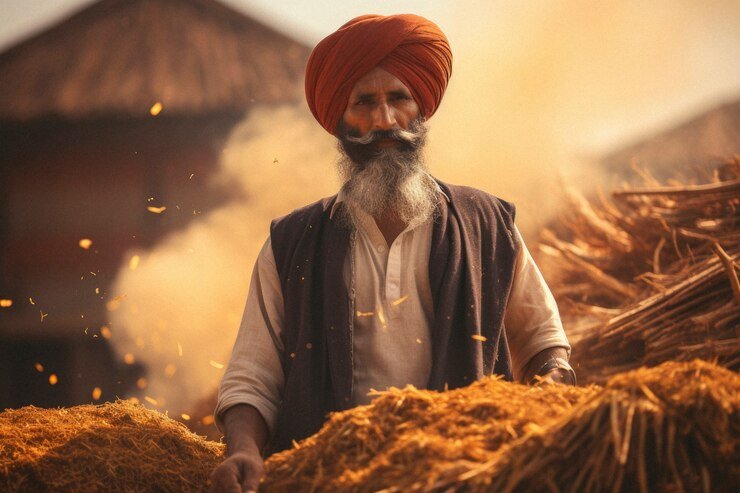
In the sprawling fields of India, where agriculture has been a cornerstone of civilization for millennia, the shift towards sustainable farming practices marks a crucial evolution. As the world grapples with environmental challenges, India’s agricultural sector stands at a pivotal juncture, poised to embrace innovation while preserving traditional wisdom.
Traditional Farming Practices
Historically, Indian agriculture has relied on time-tested methods passed down through generations. Practices such as crop rotation, mixed cropping, and organic fertilization have sustained communities and ecosystems alike. These methods not only ensured food security but also fostered a harmonious relationship with nature, promoting biodiversity and soil health.
Challenges in Indian Agriculture
Despite its rich agricultural heritage, India faces significant challenges in its farming sector. Issues like soil degradation, water scarcity, and unpredictable weather patterns threaten the livelihoods of millions of farmers. Economic pressures further exacerbate these challenges, making sustainability a critical imperative.
Transition to Sustainable Practices
Recognizing the urgent need for change, India has embarked on a journey towards sustainable agriculture. Government initiatives such as the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana and Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana are driving the adoption of modern sustainable techniques across the country. Farmers are increasingly turning to practices like integrated pest management and precision farming to optimize yields while minimizing environmental impact.
Role of Technology in Agriculture
An important factor in the transformation of Indian agriculture is technology. Enhancing productivity and resource efficiency, innovations such as AI-driven analytics, IoT-enabled devices, and remote sensing enable farmers to make data-driven decisions. In addition to streamlining agricultural operations, these technologies allow for real-time crop and soil condition monitoring, guaranteeing sustainable farming methods throughout.
Organic Farming Techniques
Organic farming has emerged as a beacon of sustainable agriculture in India. By eschewing synthetic chemicals and focusing on natural inputs, organic farmers preserve soil fertility and biodiversity. Successful initiatives like Sikkim’s transition to a fully organic state showcase the viability and benefits of organic farming on a larger scale.
Water Management Solutions
Efficient water management is crucial for sustainable agriculture in water-stressed regions of India. Techniques such as drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and canal lining are helping farmers optimize water use, reduce wastage, and mitigate the impact of droughts. These practices not only conserve precious water resources but also enhance crop resilience in the face of climate variability.
Crop Diversification
Diversifying crops is another strategy gaining traction among Indian farmers. By growing a variety of crops, farmers not only spread risks but also improve soil health through natural nitrogen fixation and pest control mechanisms. Initiatives promoting millets and pulses alongside traditional crops like rice and wheat are restoring ecological balance and promoting nutritional diversity.
Community and Cooperative Farming
Community and cooperative farming models are fostering solidarity among farmers while promoting sustainable practices. By pooling resources and sharing knowledge, these models empower smallholders to access markets, negotiate fair prices, and collectively invest in sustainable technologies. This cooperative spirit not only strengthens rural communities but also promotes equitable growth in agriculture.
Economic Viability of Sustainable Farming
Contrary to misconceptions, sustainable farming can be economically viable for Indian farmers. Studies show that investments in sustainable practices yield long-term benefits such as reduced input costs, improved soil health, and premium prices for organic produce in domestic and international markets. As consumer awareness grows, the demand for sustainably grown food continues to rise, creating new avenues for agricultural entrepreneurship.
Education and Awareness Programs
Education plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable farming practices among Indian farmers. Government-sponsored training programs, agricultural extension services, and awareness campaigns educate farmers about the benefits of sustainable practices and provide them with the skills needed to adopt new technologies. By fostering a culture of innovation and resilience, these programs empower farmers to navigate challenges and embrace sustainability.
Policy and Regulation
Robust policies and regulations are essential for driving the transition to sustainable agriculture in India. Current initiatives focus on incentivizing eco-friendly practices, subsidizing organic certification, and promoting climate-smart agriculture. However, challenges such as bureaucratic hurdles and inconsistent implementation remain barriers to widespread adoption. Looking ahead, policymakers must prioritize sustainability and collaborate with stakeholders to create an enabling environment for change.
Success Stories in Indian Agriculture
Across India, pioneering farmers are leading by example, demonstrating the transformative power of sustainable practices. From organic cotton farms in Maharashtra to integrated farming systems in Punjab, these success stories inspire others to follow suit. By sharing their experiences and lessons learned, these farmers contribute to a growing movement towards a more sustainable and resilient agricultural sector.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite significant progress, challenges persist on the path to sustainable agriculture in India. Issues such as access to finance, market volatility, and climate change require innovative solutions and collective action. Looking forward, leveraging technology, enhancing policy coherence, and empowering farmers will be crucial in overcoming these challenges and securing a sustainable future for Indian agriculture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the transition from tradition to innovation in sustainable farming is not just a necessity but a collective responsibility. By preserving ancient wisdom and embracing modern technologies, India’s agricultural sector can achieve sustainability without compromising productivity or profitability. As consumers, policymakers, and farmers unite in this endeavor, they pave the way for a greener, more resilient future where agriculture thrives in harmony with nature.
FAQs
What is sustainable farming in the context of Indian agriculture?
Sustainable farming in India refers to agricultural practices that aim to preserve the environment, support economic viability, and enhance social well-being over the long term.
How is technology influencing sustainable farming practices in India?
Technologies such as IoT, AI, and remote sensing are empowering farmers with data-driven insights to optimize resource use, monitor crops, and improve productivity sustainably.
Why is water management critical in sustainable agriculture?
Efficient water management ensures that farmers can sustainably use water resources, mitigate risks from climate variability, and enhance crop resilience.
What part do laws and regulations play in encouraging sustainable farming in India?
In order to lessen their influence on the environment, farmers are encouraged by government laws to embrace sustainable farming methods, support organic farming, and make investments in climate-smart agriculture.
How can Indian consumers help promote sustainable farming practices?
By purchasing organic, locally grown food, supporting fair trade policies, and spreading awareness of the advantages of sustainable agriculture, consumers may help promote sustainable farming.